Gas Exchange
Water enters the gill chamber at the
base of the cheliped like in all other crabs. The water that passes
through this entrance is filtered by setae which sit at the base of
the chelipeds, a feature that all benthic crabs have to remove
sediments from the inhalant flow. A current is created by the gill
bailer which pulls water into the inhalant chamber. Once there, water
flows across the gill filaments and then through to the exhalant
chamber. The water then exits anteriorly through exhalant apertures.
In summary the water that passes through the branchial chamber
follows a U shape, entering in the posterior direction and exiting
anteriorly after passing through the gill filaments, (see Figure 17.) Gas exchange
occurs by diffusion across a very thin cuticle, to the deoxygenated
blood supplied by veins. Clibanarius longitarus in particular, like
many other anomurans, have plate-like lamellae gill filaments, (see Figure 17.) The
gill filaments in decapods are cleaned by elongated epiopods of the
three maxillipeds, which sweep the filaments of any foreign
particles, (Ruppert, Fox & Barnes, 2004.)
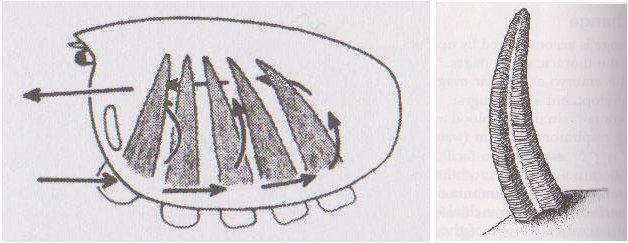
Figure 17- (left) Diagram showing the flow direction of water through the gill chamber. (right) Diagram of the gill lamellae found in in the Blue striped hermit crab. (Diagrams modified from Ruppert, Fox & Barnes, 2004, by Author, 2014) |